As parenterally administered drugs, gene therapies must undergo the same rigorous safety testing required by the FDA for protein therapeutics. This includes characterising the stability of the vector by monitoring the formation of subvisible particles that can also lead to adverse immunogenic events.
Subvisible particle measurements are a stability predictor that minimises risk and enables more informed decisions about viral vector formulations and quality assessment. Backgrounded Membrane Imaging (BMI) on the Aura GT system detects how parameters like freeze-thaw cycles, ionic strength, and different additives influence vector stability to determine optimal formulation and storage conditions for your gene therapy product.
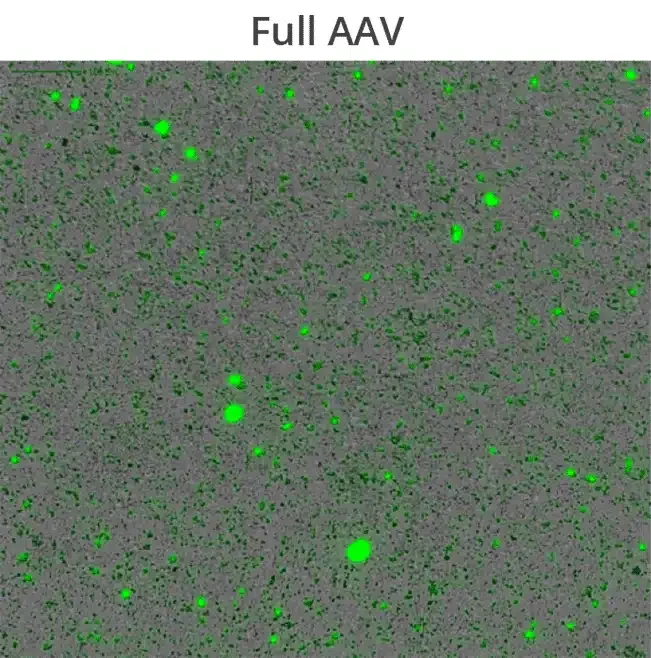
Additionally, compromised capsid integrity can result in DNA leakage which promotes aggregate formation, potentially lowering product purity and significantly reduce drug efficacy. Understanding how capsid proteins interact with leaked DNA payloads is essential to avoid vector aggregation and ensure high quality drug product development, control, and shelf-life.
Aura GT’s BMI technology allows high-throughput subvisible imaging, counting and size distribution, and fluorescence applications ID capsids, aggregates and track DNA leakage to determine viral vector stability.